MLCC Slurry: Introduction to Depth Filtration Technology
2025-03-25
MS
38
Multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC), as a critical component in electronic devices, is widely used in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial control fields. The performance and reliability of MLCC are highly dependent on its manufacturing processes, with slurry filtration technology (see Figure 1) being a crucial step to ensure product quality.
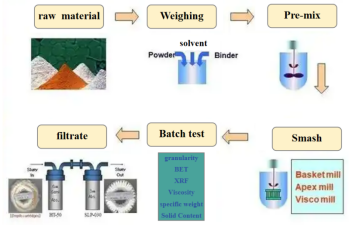
Figure 1: Slurry Preparation Proces
Composition of MLCC Slurry
MLCC slurry is primarily composed of ceramic powder, solvent, binder, dispersant, plasticizer, and defoamer.
Ceramic powder: Provides dielectric properties. Barium titanate (BaTiO?) is commonly used. After sintering, it hardens and becomes brittle, forming a polycrystalline and multiphase ceramic structure. This material is the decisive factor in product quality.
Solvent: Wets the ceramic powder, enabling better and more uniform integration with the binder to achieve appropriate viscosity.
Binder: Through ball milling or sand milling, the binder uniformly coats each ceramic powder, imparting adhesion to form qualified membrane sheets.
Dispersant: Also known as a deflocculant or peptizer, an interfacial active agent with two opposite properties of lipophilicity and hydrophilicity within its molecules. It can form an adsorption layer on the surface of ceramic powder particles, increase the zeta potential of the slurry system, and thereby enhance the reaction force between particles that form steric hindrance, improving the fluidity of the slurry.
Plasticizer: Reduces the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the binder, increasing its fluidity and imparting flexibility to the adhesive film.
Defoamer: Exhibits low surface tension and high surface activity. Though insoluble in foaming media, it disperses uniformly to suppress or eliminate foam.
MLCC slurry particles are small (0.2~5μm) and tend to agglomerate due to Van der Waals' forces, surface energy, and electrostatic interactions (see Figure 2). Agglomerates in the slurry can cause internal defects in MLCC, affecting electrical performance and reliability. Depth filtration technology effectively removes such impurities, ensuring slurry uniformity and stability.
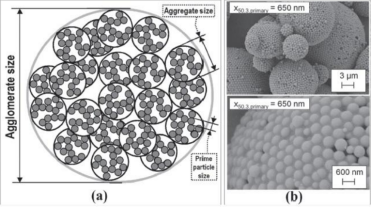
Figure 2: Slurry Particle Agglomeration
Principles and Advantages of Depth Filtration for MLCC
Depth filtration technology leverages the porous, multilayered structure of filter media to remove impurities and agglomerates from the slurry through mechanisms such as physical interception, adsorption, and inertial collision. Unlike surface filtration, depth filtration captures smaller particles and offers higher dirt holding capacity.
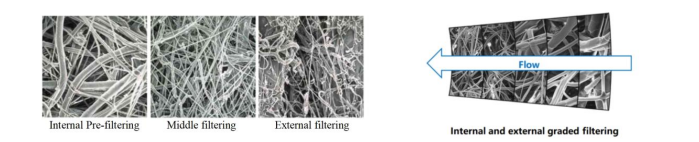
Figure 3: Structural Principle of Depth Filtration
Advantages of Depth Filtration: (1) High filtration accuracy (removal ratings), capable of effectively removing small particles and agglomerates; (2) High dirt holding capacity, porous structure can accommodate a large amount of impurities, extending the service life of the filtration media; (3) Suitable for high viscosity slurries, maintaining high filtration efficiency for high viscosity MLCC slurries.
Membrane Solutions’ CMPro-L Series and PPD Series, specifically designed for MLCC slurry filtration, utilize composite-structured polypropylene filter media. Their unique gradient design efficiently intercepts large particles and agglomerates in MLCC slurries while minimizing the removal of functional particles. With a service life more than twice that of conventional filter cartridges, these products reduce replacement frequency and lower operational costs for customers.
